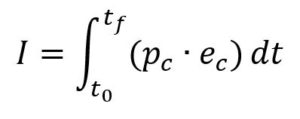OVERVIEW
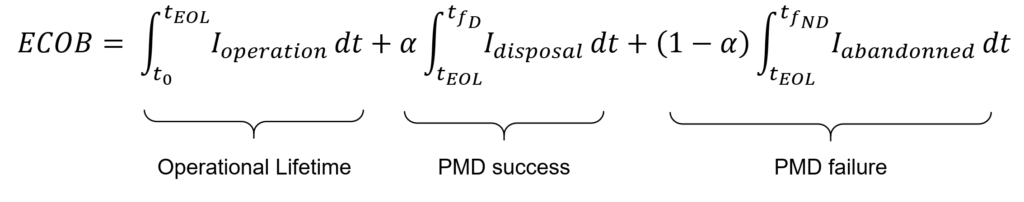
The mission index module of the SSR is directly derived from the European Space Agency debris index and quantifies the level of harmful physical interference caused by the planned design and mission operation. It measures the impact of a space mission on the space environment, using the Environmental Consequences of Orbital Breakups (ECOB) formulation. ECOB is a risk indicator built from the general expression considering mission characteristics, collision avoidance strategy, post mission disposal strategy and success rate.
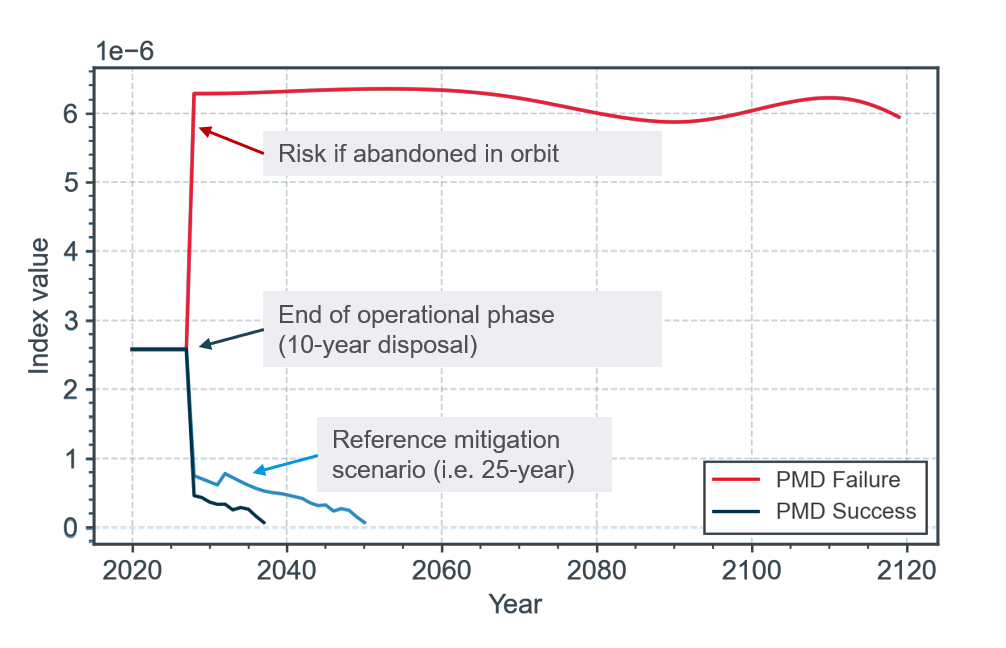
The index value (I) is a risk indicator computed using a model simulating the state and behaviour of all space objects including the planned mission. This index value is normalized considering the space environment capacity in order to provide a score for the module between 0 and 1 (a high index i.e. a strong impact on the space environment results in a low score).
Here below is a simplified formulation of the index:
Where the probability term pc captures the likelihood that an object is involved in a collision event and the severity term ec quantifies the consequences of such an event.
Index formulation
Mission index required input summary
The mission index is a quantifiable metric of the consumption of the space environment based on well-known mission parameters. The inputs requested from the SSR applicants are:
- Satellite and mission design
- Number of satellites
- Mass of the satellites
- Cross sectional area
- Deployment duration
- Planned Orbital lifetime
- Orbital parameters
- Operational mean altitude
- Inclination
- Post Mission disposal strategy
- Targeted end of life apogee and perigee altitude
- Expected post mission disposal success rate
- Collision avoidance strategy
- Accepted collision probability level
- Lead Time
As it stands, the mission index is computed by the space debris office at ESA, but a direct integration of the computation method within the rating platform is foreseen in 2023.